Dealing With Bullying
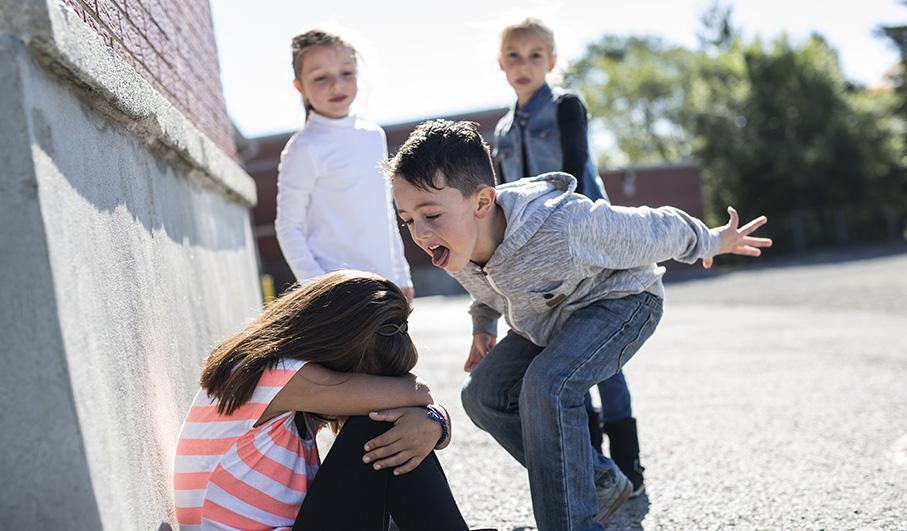

Being bullied can make an ordinarily happy child miserable, and the after effects of bullying can last well into adulthood. This brief guide will help you to identify types of bullying and warning signs that your child is being targeted, as well as how best to deal with bullying situations.
What is bullying?
Bullying is social aggression in which an individual or group targets another child or children for intentional abuse. The target of bullies might appear unlikely to retaliate or act in self-defense. Bullying might be physical (such as hitting or destroying his or her belongings), but it can also be verbal, psychological or social, such as saying cruel things.
The harmful effects of bullying on child development
Bullying in young children can cause mental health issues, including low self-esteem, regression, anxiety and trouble sleeping. Bullied children might be too preoccupied to pay attention, resulting in low attention spans in class.
Signs your child is being bullied
Recognizing and understanding bullying helps you deal with it properly. If your child often loses his or her belongings, is acting out of sorts, is showing a lack of interest in school or a fear of school or has frequent physical complaints, these are all signs of possible bullying.
Parenting tips for dealing with bullying
Find out as much as you can, including the nature of the bullying and how your child has responded. Teach your child not to retaliate violently. Encourage seeking an adult’s help or ignoring the bully if possible.
Because bullying negatively impacts child development, it is important to act. Note down every detail of the situation and speak to your child’s teacher or the school’s guidance counselor. Convey your concerns politely but persist if the school doesn’t address the situation. Also find out the school’s policy regarding bullying, and suggest changes if it is insufficient.













 Parenting Articles
Parenting Articles

